◇◆
Tagging Tables
Table, Table Wrapper, and Table Group
There are three similar sounding elements for tagging tables:
|
The element containing the rows and columns of tabular table material. The Tag
Suite default element is <table>, taken
from the JATS XHTML-inspired table model. The OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) table
model can also be used with the Tag Suite, and the name for the similar
rows-and-columns element is typically
“<oasis:table>”.
|
|
|
Element that represents the complete table. This includes the row-and-column
data, table number, table caption including the table title, and any table footnotes
or general notes attached to the table. If the complete table includes a label (such
as “Table 3”) and it should appear in a List of Tables for the
publication, then it is tagged with the <table-wrap> element.
|
|
|
A logical or display grouping of more than one complete table (<table-wrap>).
|
Table Wrapper
Simply put, the <table-wrap> is a
container for tables. Here is a <table-wrap> element that contains nothing but a BITS <table> element inside it:
...
<table-wrap>
<table frame="box">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Color</th>
<th>Size</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td rowspan="3">Green</td>
<td>small</td>
<td>$3.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>medium</td>
<td>$2.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>large</td>
<td>$1.15</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td rowspan="3">Red</td>
<td>small</td>
<td>$3.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>medium</td>
<td>$5.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>large</td>
<td>$9.95</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</table-wrap>
...
The <table-wrap> element also provides
a uniform place to put information such as a table number (<label>) and table title and caption (both in
<caption>). The element <table-wrap> can also contain a Table Wrapper Footer, as a place to put table footnotes and
other information.
<table-wrap id="TN0.170"> <label>Table 17. </label> <caption> <title>Patient Care at End of Follow Up</title> <p>Numbers of patients receiving institutional care at the end of scheduled follow up and use of hospital beds among those allocated to day hospital or alternative services</p> </caption> <table frame="box" rules="all" cellpadding="5">...</table> <table-wrap-foot> <fn-group> <fn id="TF1-150"><p>Data not available for 1 trial.</p></fn> <fn id="TF1-151"><p>P<0.05 (random effects model).</p></fn> </fn-group> </table-wrap-foot> </table-wrap>
Nested Tables
The table models in BITS do not allow nested tables. That is, a table cell (e.g.,
<td>) may not contain a table. However, table cells may contain <array>s. This allows a table cell to contain nested row/column structures but does not allow
a table cell to contain tables with caption, headers, and such.
Non-tabular Tables
It is possible that a <table-wrap> will not contain a <table> element at all, since objects that are identified as tables need not contain tabular
material. While a <table-wrap> may contain
the rows and columns of a table element as just shown (using either the NISO JATS
XHTML-inspired Table <table> or the OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) table model
<oasis:table>), in place of explicit table elements, a table may contain only:
- one or more graphics,
- a bulleted or numbered list,
- a definition list,
- paragraphs of material, or
- a mixture of these elements.
Here is a table that has no tabular material in it because the tabular portion is
represented as a graphic:
... <table-wrap id="Table-07"> <caption> <title>2008 Expenditures</title> <p>Total research expenditures by disease, 2008</p> </caption> <graphic xlink:href="totals.jpeg"> <alt-text>Distribution of research spending for major diseases.</alt-text> <object-id>314159</object-id> </graphic> <attrib>Reprinted courtesy of TableSource, Inc.</attrib> </table-wrap> ...
Here is another non-tabular table:
<table-wrap id="Table-05"> <caption> <title>Show and Tell Program</title> </caption> <list list-type="order"> <list-item><label>1.</label><p>Poodle</p></list-item> <list-item><label>2.</label><p>Persian Cat</p></list-item> <list-item><label>3.</label><p>Weaver Finches</p></list-item> <list-item><label>4.</label><p>Gecko</p></list-item> </list> <attrib>Reprinted courtesy of YourSchool.edu</attrib> <permissions> <copyright-statement>© 2008</copyright-statement> </permissions> </table-wrap>
Table Group
Some complex tables may consist of a single table wrapper (<table-wrap>) containing a one or more small tables
that represent one logical tabular area. For example, one part of the display might
be
3 rows by 10 columns, the next part might be 5 rows by 2 columns, and the last part
may return to 10 columns for 6 more rows. Each tabular area can be tagged with a BITS
<table> element (or an OASIS XML
Exchange (CALS) <oasis:table> element), and paragraphs of text may
be interspersed between the tabular material. In the United States, tax tables are
frequently this type of table.
In the example just explained, three <table>s equaled one <table-wrap> and not a <table-wrap-group>. A
<table-wrap-group> contains multiple
<table-wrap> elements, each of which
typically has a table number, caption or title, and tabular material. The entire group
may also be given a collective label and caption. Table groups are frequently a print
artifact, where several tables are clustered on a page for better display. The
<table-wrap-group> element has been
provided to capture these as well as semantic or logical groupings. Here is an
abbreviated <table-wrap-group>:
... <table-wrap-group id="Table-grp-06"> <label>Special Section II.</label> <caption><title>Tables 3 through 5</title></caption> <table-wrap id="Table-03"> <label>Table 3</label> <caption><p>...</p></caption> <graphic xlink:href="..."></graphic> </table-wrap> <table-wrap id="Table-04"> <label>Table 4</label> <caption><p>...</p></caption> <graphic xlink:href="..."></graphic> </table-wrap> <table-wrap id="Table-05"> <label>Table 5</label> <caption><p>...</p></caption> <graphic xlink:href="..."></graphic> </table-wrap> </table-wrap-group> ...
Table Formatting
By default, this Tag Set uses the JATS XHTML-inspired table model (based on and
designed to be converted easily to the XHTML Table Model). This model matches the
needs of web browsers and can support (at least roughly) most table display
formatting.
Format is indicated in one of two ways in a BITS default table: using multiple
single-purpose attributes for simple formatting, or making more complex formats using
the
@style attribute.
Simple Formatting with Attributes
Simple format information can be indicated with the following attributes:
- @border controls borders around all of the cells in a table,
- @cellpadding controls space between the text and any borders in the cells of the table,
- @cellspacing controls space between the cells of the table,
- @frame controls the “box” around the whole table,
- @rules controls rules between groupings in the table (rows, columns, column groups, etc.), and
- @width controls the width of the entire table or columns within the table.
To illustrate use of the @rules
attribute, here is a table with rules on the rows:
...
<table-wrap>
<table rules="rows">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Color</th>
<th>Size</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td rowspan="3">Green</td>
<td>small</td>
<td>$3.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>medium</td>
<td>$2.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>large</td>
<td>$1.15</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td rowspan="3">Red</td>
<td>small</td>
<td>$3.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>medium</td>
<td>$5.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>large</td>
<td>$9.95</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</table-wrap>
...
Here is the same table, without the rules, to demonstrate use of the @frame attribute:
...
<table-wrap>
<table frame="box">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Color</th>
<th>Size</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td rowspan="3">Green</td>
<td>small</td>
<td>$3.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>medium</td>
<td>$2.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>large</td>
<td>$1.15</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td rowspan="3">Red</td>
<td>small</td>
<td>$3.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>medium</td>
<td>$5.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>large</td>
<td>$9.95</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</table-wrap>
...
And here is the @border
attribute:
...
<table-wrap>
<table border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Color</th>
<th>Size</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td rowspan="3">Green</td>
<td>small</td>
<td>$3.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>medium</td>
<td>$2.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>large</td>
<td>$1.15</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td rowspan="3">Red</td>
<td>small</td>
<td>$3.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>medium</td>
<td>$5.25</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>large</td>
<td>$9.95</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</table-wrap>
...
Formatting with Style
All the tables just shown are all relatively simple formats. More complex table
formatting is done using the @style
attribute, which contains CSS instructions. Key to understanding how the CSS in tables
works is that instructions on smaller portions override those on larger portions of
the
table. For example, if a background color is provided for the whole table and a different
background color is specified for a row, everything in the table will be the first
background color except that row, which will have the second. Similarly, if borders
are
specified for a <colgroup>, they will apply
to the whole <colgroup> unless a different
border is specified for one cell (<th> or
<td>), in which case that cell will have
the override.
Here is a sample, in code and image, of a relatively complex table, formatted using
a variety of techniques including CSS in the @style attribute, controlling alignment with the @align attribute, and a few spans.
... <table-wrap> <table rules="groups"> <colgroup style="border-right: hidden"><col/></colgroup> <colgroup style="border-right: solid thin"><col/><col/><col/></colgroup> <colgroup><col/><col/><col/></colgroup> <tr> <th></th> <th colspan="3" style="border-bottom: solid">1974-75</th> <th colspan="3" style="border-bottom: solid">1983-84</th> </tr> <tr> <th></th> <th style="border-bottom: solid thin">Public</th> <th style="border-bottom: solid thin">Private</th> <th style="border-bottom: solid thin">Total</th> <th style="border-bottom: solid thin">Public</th> <th style="border-bottom: solid thin">Private</th> <th style="border-bottom: solid thin">Total</th> </tr> <tr> <td style="background: lightgrey" colspan="7">Preschool</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Schools</td> <td align="right">n.a.</td> <td align="right">n.a.</td> <td align="right">n.a.</td> <td align="right">n.a.</td> <td align="right">n.a.</td> <td align="right">n.a.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Teachers</td> <td align="right">2,986</td> <td align="right">1,252</td> <td align="right">4,238</td> <td align="right">15,440</td> <td align="right">4,008</td> <td align="right">19,448</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Enrollment</td> <td align="right">108,500</td> <td align="right">43,800</td> <td align="right">152,300</td> <td align="right">442,700</td> <td align="right">80,600</td> <td align="right">523,300</td> </tr> <tr> <td style="background: lightgrey" colspan="7">Primary</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Schools</td> <td align="right">9,982</td> <td align="right">1,116</td> <td align="right">11,098</td> <td align="right">11,397</td> <td align="right">1,285</td> <td align="right">12,682</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Teachers</td> <td align="right">54,276</td> <td align="right">8,922</td> <td align="right">63,198</td> <td align="right">71,454</td> <td align="right">9,176</td> <td align="right">80,630</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Enrollment</td> <td align="right">1,764,100</td> <td align="right">226,000</td> <td align="right">1,990,100</td> <td align="right">2,338,400</td> <td align="right">303,000</td> <td align="right">2,641,400</td> </tr> <tr> <td style="background: lightgrey" colspan="7">Secondary</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Schools</td> <td align="right">735</td> <td align="right">438</td> <td align="right">1,173</td> <td align="right">1,486</td> <td align="right">710</td> <td align="right">2,196</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Teachers</td> <td align="right">24,222</td> <td align="right">9,133</td> <td align="right">33,355</td> <td align="right">41,350</td> <td align="right">13,964</td> <td align="right">55,314</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Enrollment</td> <td align="right">513,100</td> <td align="right">118,100</td> <td align="right">631,200</td> <td align="right">786,200</td> <td align="right">177,200</td> <td align="right">963,400</td> </tr> <tr> <td style="background: lightgrey" colspan="7">Higher Education</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Schools</td> <td align="right">26</td> <td align="right">12</td> <td align="right">38</td> <td align="right">535</td> <td align="right">275</td> <td align="right">805</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Teachers</td> <td align="right">13,228</td> <td align="right">1,376</td> <td align="right">14,604</td> <td align="right">24,633</td> <td align="right">4,072</td> <td align="right">28,705</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Enrollment</td> <td align="right">172,100</td> <td align="right">21,200</td> <td align="right">193,300</td> <td align="right">320,800</td> <td align="right">63,900</td> <td align="right">384,700</td> </tr> </table> </table-wrap> ...
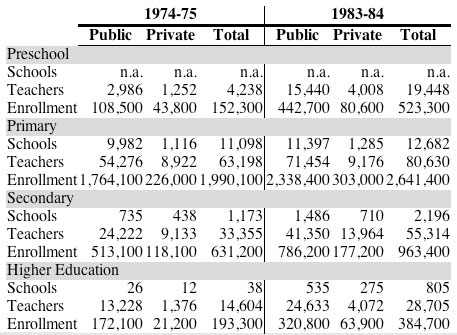
Table Models
By default, this Tag Set uses the XHTML-inspired table model, as defined in the NISO
JATS XHTML-inspired Table Module. However, this Tag Set can be set up to use the OASIS
XML
Exchange (CALS) table model either instead of or in addition to the XHTML-inspired
model.
The modules that enable the OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) table model are distributed
as part
of this Tag Set, and a separate OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) Table Tag Library
(https://jats.nlm.nih.gov/options/OASIS/tag-library/19990315/index.html)
describes the OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) table model elements, attributes, and parameter
entities.
To enable two different tagging schemes for the same material (row and column tables),
all OASIS elements have been given a namespace and use the namespace prefix
“oasis”. Since DTDs do not really work with namespaces, the
namespace prefix has been hard-coded into the names of the OASIS table elements. This
differentiates the two sets of table elements, allowing both XHTML-inspired and OASIS
XML
Exchange (CALS) table models to be used together in a single XML document.
To illustrate how this works and for use by the user community, a separate OASIS XML
Exchange (CALS) table BITS Book DTD is available as part of this Tag Set. It uses
the
OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) table elements in addition to the JATS XHTML-inspired table
elements (filename BITS-book-oasis2-1.dtd).
NISO JATS XHTML-inspired Table: The modules that
implement the XHTML-inspired Table coding are:
- The JATS XHTML-inspired Table Setup Module (JATS-XHTMLtablesetup1-3.ent) Sets
all parameter entities needed by the JATS Table Module, and then references
(invokes) the XHTML-inspired Table Module. (See next item.)
To include the JATS table model in a tag set, a DTD must reference this module.
- XHTML-inspired Table Module (xhtml-table-1.mod) The public XML DTD version of the XHTML Table Module. This contains the JATS version of the W3C-developed XHTML table model. This module is invoked from the module JATS-XHTMLtablesetup.ent. (See previous item.)
- XHTML-inspired Table Style Module (xhtml-inlstyle-1.mod) Declares the @style attribute, which supports inline style markup for elements such as <td> and <tr> within XHTML-inspired Table.
OASIS CALS Tables: The XHTML-inspired table model is
the JATS default, but a DTD has been provided for archives and publishers that use
OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) table model. As set up, this is a separate DTD that defines
both
the XHTML-inspired and the OASIS Exchange (CALS) table models, with the OASIS table
model
namespaced (prefix “oasis”) to prevent name clashes. An XML
expert can readily turn off the JATS XHTML-based model and (once there is only the
single OASIS Exchange (CALS) table model) remove the OASIS namespace using NISO
JATS-provided overrides (the OASIS Table Module need not be touched). The following
files
are necessary to use the OASIS Exchange (CALS) table model:
- Book Interchange DTD with OASIS and XHTML Tables (BITS-book-oasis2-1.dtd) Complete BITS DTD for the creation of new books. This extension of the BITS Book DTD replaces the BITS Book DTD module and invokes both the XHTML table and the CALS OASIS XML Exchange Table models.
- The BITS Book Interchange DTD-Specific Modules with OASIS and XHTML Tables (BITS-book-oasis-custom-modules2-1.ent) The DTD-specific modules for the new BITS Book DTD that includes both the OASIS Tables and the XHTML-like Tables.
- The BITS Book Interchange DTD with OASIS and XHTML Tables Customize Classes Module (BITS-book-oasis-custom-classes2-1.ent) The class overrides for this new Book DTD. These repeat all the class overrides of the regular BITS Book DTD, with the table and alternative classes modified to use the OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) table elements as well as the XHTML-like elements. There is no equivalent mix override module, because this DTD uses the ordinary BITS Book mix overrides.
- JATS OASIS Table Namespace Module (JATS-oasis-namespace1-3.ent) This module establishes the prefix for the OASIS Exchange (CALS) table model, by default “oasis” (“<oasis:table>”).
- JATS Namespaced OASIS XML Table Setup Module (JATS-oasis-tablesetup1-3.ent) Sets all parameter entities needed by the OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) table model, and then references (invokes) the OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) Table Model Module for declarations of all the table elements.
- OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) Table Model Module (oasis-exchange.ent) This is the OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) table model DTD fragment, modified to use the OASIS namespace with the “oasis” prefix. This module is invoked from the JATS OASIS XML Exchange (CALS) setup module.